- Social Network Analysis: community detection can be used to study human interaction and collective behaviour on a massive scale, analyze the transfer of information, and gain insights into the attitudes and opinions between individuals. It can also be used for targeted advertising and market segmentation.3,4
- Criminology: community detection can be used for bot (i.e., software robots that impersonate human activity) identification, and to detect other suspicious or criminal activity online.5
- Public Health: community detection can be used for discovering groups susceptible to an epidemic disease, or to study genomic data with respect to different types of cancer.2,6
How Does Community Detection Work?
Complex networks are modelled as graphs. A graph is a mathematical object consisting of nodes and edges. Nodes can be used to represent individuals in a network and edges can represent the relationships (links) between individuals.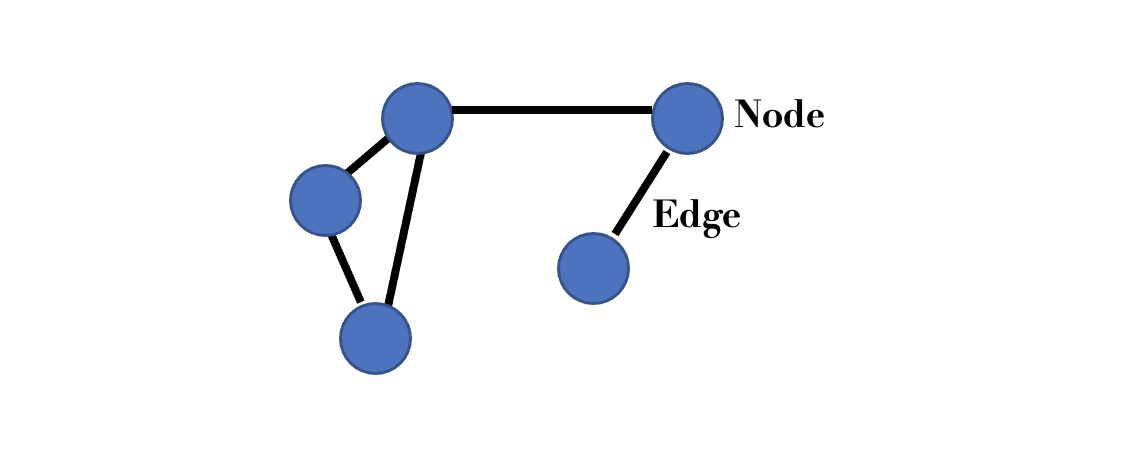
Figure 1: Simple example of a graph with five nodes and five edges.
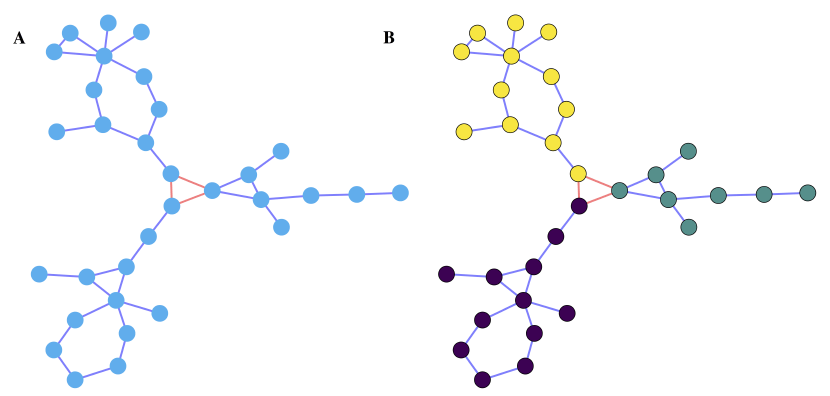
Figure 2: Example of a graph consisting of 32 nodes divided into three clusters of 8, 12, and 12. The nodes represent users that are connected by purple or orange edges, denoting a positive or negative relationship between them, respectively.
Quantum Computing Applied to Community Detection
As quantum hardware matures, running quantum algorithms on a large scale will become possible. At that point, quantum computers could solve larger, commercially relevant problems involving community detection in large and complex networks. Such problems are impossible to analyze currently using conventional (our everyday, non-quantum, or “classical”) computers. In a recent study,1 1QBit researchers developed a community detection algorithm that runs on both classical and quantum computers. They have verified their approach on small networks. The fact that the proposed algorithm runs on conventional computers is a useful feature, as classical computers are significantly more powerful than quantum computers at present. For this reason, a person can immediately use the developed algorithms to discover communities within graphs of a meaningful size while awaiting the arrival of more-powerful quantum computers. Quantum computers are built with quantum bits, or qubits, to process information. Qubits are any two-level microscopic system that is subject to the effects of quantum physics. Qubits are different from bits because they can be in a what is known as a quantum superposition (a sort of combination), of the two states 0 and 1, and can therefore have more information encoded in them. The amount of information increases exponentially with the number of qubits that are connected in the system. How does community detection on a quantum computer work? In basic terms, in order to run the algorithm on a quantum computer, nodes are encoded into qubits, and the edges are treated as the couplings between qubits. Once a problem has been mapped into a quantum computer, it runs the algorithm. After the run finishes, it is possible to look into the information encoded into each qubit. Using this information, the authors of the study1 were able to assign each node to its specific community. So, why did the researchers try this new method in the first place? In addition to running on both classical and quantum computers, their approach has two advantages over traditional community detection methods:- Traditional methods tend to solve the community detection problem by breaking a larger graph into smaller parts and analyzing them separately. This creates artificial boundaries between the discovered communities, whereas the researchers’ algorithm preserves the overall network structure.
- Their algorithm automatically finds the optimal number of communities in a given graph without needing to rely on prior knowledge of the number of communities present.
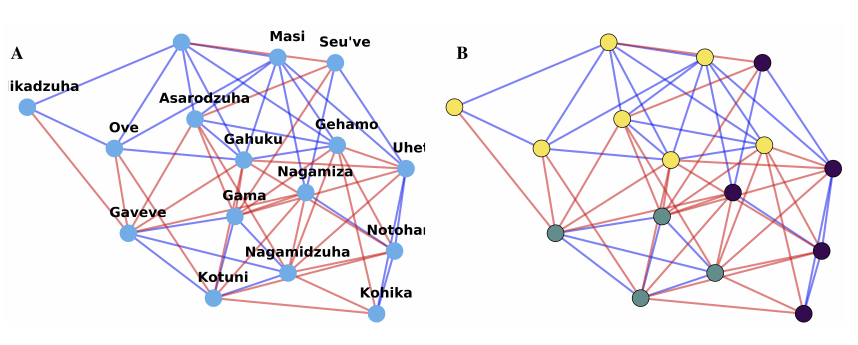
Figure 3: Community detection problem for a real-world dataset.1 The relation between tribal groups of the Eastern Central Highlands of New Guinea is shown. The tribal groups are represented using nodes. Purple links denote a friendly relation between groups. Orange links denote an antagonistic relation between groups.
What’s Next for Community Detection Using Quantum Hardware?
As a next step, the researchers are looking to tackle larger datasets for real-world applications. The goal is to use their method on complex, real-world networks for practical applications, such as in social networks, telecommunications, medical science, or protection against criminal activity. In the future, the power, and thereby the usefulness, of the quantum version of the method will scale up with the number of available qubits in quantum computers. To learn about the quantum community detection method in more detail, read the article. And, to stay informed of other developments in advanced and quantum computing, subscribe to the 1QBit blog.References
1 E. Zahedinejad, D. Crawford, C. Adolphs, and J. S. Oberoi, “Multi-Community Detection in Signed Graphs Using Quantum Hardware”, arXiv:1901.04873, (2019).
2 M. Salathé, and J. H. Jones, “Dynamics and Control of Diseases in Networks with Community Structure,” PLoS Computational Biology, 6, 4, (2010).
3 C. Wang, W. Tang, B. Sun, J. Fang, and Y. Wang, “Review on Community Detection Algorithms in Social Networks,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Progress in Informatics and Computing, 551–555, (2015).
4 A. Karataş, and S. Şahin, “Application Areas of Community Detection: A Review”, Int. Cong. on Big Data, Deep Learning and Fighting Cyber Terrorism, 65–70, (2018).
5 A. Karataş, and S. Şahin, “A Review on Social Bot Detection Techniques and Research Directions,” in Proc. Int. Security and Cryptology Conference, 156–161, (2017).
6 N. Haq, and Z. J. Wang, “Community Detection from Genomic Datasets Across Human Cancers” IEEE Global Conf. on Signal and Infor. Process., 1147–1150, (2016).